| Table of Contents |
|---|
OpenSpecimen helps to capture the entire lifecycle of the specimens starting from the collection, processing, storage, and distribution. This page explains different features of OpenSpecimen to add specimen information in different various scenarios. Below are the highlights:
- Lineage of specimens: After collection, specimens are often processed into different forms for storage. For example, Blood is collected and processed into Plasma, PBMC, and Buffy Coat. In OpenSpecimen, each level can be indicated as a ‘specimen’ as primary, derivative, or aliquot.
- Hierarchy of the specimens: To indicate the lineage of specimens, ‘specimen tree’ can be viewed in OpenSpecimen.
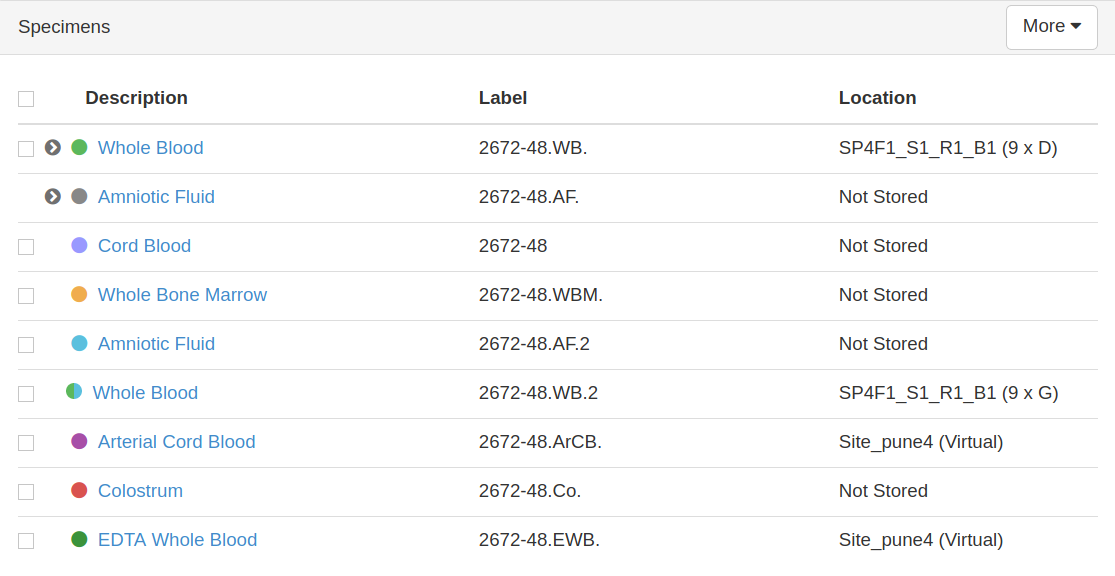
- Different status of the specimen: A color-coding scheme for specimens , allows you to quickly identify the status of a specimen as to whether it is collected, stored, distributed, or discarded. For more details, refer to the specimen color - coding section in on this page.
- Default specimen annotations: Generic details like specimen type, anatomic location, quantity, etc., are captured in default data entry pages.
- Custom annotations: Additional annotations like test results and pathology annotations can be captured using custom forms.
- Planned collection: For studies where what type of specimens is collected and how it is processed is known in advance, the protocol can be set up with all details so that to make data entry is simpler.
- Unplanned collection: When specimen collection details are unknown, they can be entered as unplanned specimens.
...
Planned Specimen Collection
In the case of longitudinal collections, specific time-points for collection, specimen requirements, and processing details are defined at the start of the study. For this, the The planned collection workflow of OpenSpecimen allows you to define study calendars and define an SOP of the study.
For more details, refer to Planned specimen collection
...
Unplanned
...
Specimen Collection
Collections for general biobanking are usually unplanned, i.e., there are no specific time-points, and specimens get collected whenever they are available. For such cases, the unplanned specimen collection workflow of OpenSpecimen is best suited.
...
Depending on the needs or availability, you may often have to create a child or grandchild of a sample without prior planning. For such cases, OpenSpecimen allows you to collect additional derivative derivatives or aliquot aliquots from a specimen’s overview page.
...
For more details, refer to Bulk operation on specimens
Scanning
...
Specimens using Box Scanners
In high-throughput labs, the use of scanners is quite common. OpenSpecimen allows collecting specimens in bulk using box scanners.
For more details, refer to Scanning specimens from box scanners
Bulk
...
Import Specimen Data
In the case of high-throughput biobanks, the data for thousands of specimens may need to be entered. For this, OpenSpecimen allows importing data in the form of CSV files.
For more details, refer to specimens CSV
Moving
...
Specimens from
...
One Visit to
...
Another
OpenSpecimen allows you to move the specimen from one visit to another to handle the situations like merging of multiple sub-studies, accidental collection of specimens under the wrong participant/visit, etc. This can be done across collection protocols, across participants, or across the participant visits.
For more details, refer to Moving primary specimens from one visit to another.
Specimen
...
Color Coding
OpenSpecimen displays the color code for specimens based on its status.
| Expand | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
...